Готовые презентации на тему:
- Образование
- Искусство и Фото
- Наши презентации
- Авто/мото
- Технологии
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Карьера
- Данные и аналитика
- Дизайн
- Устройства и комплектующие
- Экономика и Финансы
- Машиностроение
- Развлечения и Юмор
- Путешествия
- Eда
- Политика
- Юриспруденция
- Здоровье и Медицина
- Интернет
- Инвестиции
- Закон
- Стиль жизни
- Маркетинг
- Мобильные технологии
- Новости
- Недвижимость
- Рекрутинг
- Розничная торговля
- Таможня, ВЭД, Логистика
- Наука
- Услуги
- Программное обеспечение
- Спорт
- Музыка
- Шаблоны презентации
- Детские презентации
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- История
- Литература
- Информатика
- Математика
- Обществознание
- Русский язык
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- МХК
- ОБЖ
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Технология
- Начальная школа
- Раскраски для детей
- Товароведение
- Менеджмент
- Страхование




![C# constructors
syntax:
[access-modifier] class-name ([parameters list])
{
constructor-body
};
[access-modifier] – public;
class-name – the same name as the class, where constructor is created;
[parameters list] – optional;](/documents_6/810543cd96960183e939a9377fa60851/img3.jpg)
![namespace ConsoleApplication1
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class MyClass
{
public string Name;
public byte Age;
// Constructor with parameters
public MyClass(string s, byte b)
{
Name = s;
Age = b;
}
public void reWrite()
{
Console.WriteLine(“Имя: {0}\nВозраст: {1}", Name, Age);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClass ex = new MyClass("Alexandr", 26);
ex.reWrite();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}](/documents_6/810543cd96960183e939a9377fa60851/img4.jpg)

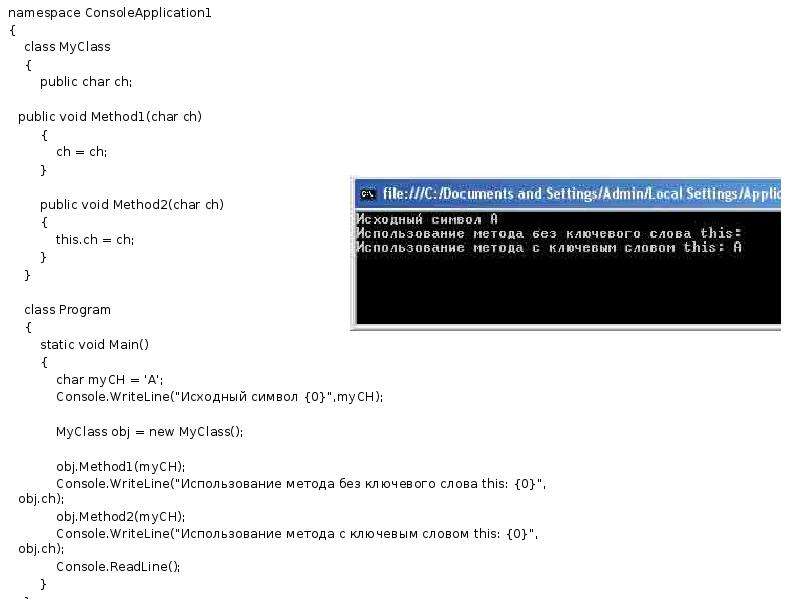

![namespace ConsoleApplication1
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class myCircle
{
// 2 methods return area and long of circle
public static double SqrCircle(int radius)
{
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
public static double LongCircle(int radius)
{
return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int r = 10;
// Use the methods of another class without creation an instance of this class Console.WriteLine("Площадь круга радиусом {0} = {1:#.##}",r,myCircle.SqrCircle(r));
Console.WriteLine("Длина круга равна {0:#.##}",myCircle.LongCircle(r));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}](/documents_6/810543cd96960183e939a9377fa60851/img8.jpg)


![namespace ConsoleApplication1
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
static class MyMath
{
static public int round(double d)
{
return (int)d;
}
static public double doub(double d)
{
return d - (int)d;
}
static public double sqr(double d)
{
return d * d;
}
static public double sqrt(double d)
{
return Math.Sqrt(d);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Исходное число: 12.44\n\n--------------------\n");
Console.WriteLine("Целая часть: {0}",MyMath.round(d: 12.44));
Console.WriteLine("Дробная часть числа: {0}",MyMath.doub(d: 12.44));
Console.WriteLine("Квадрат числа: {0:#.##}",MyMath.sqr(d: 12.44));
Console.WriteLine("Квадратный корень числа: {0:#.###}",MyMath.sqrt(d: 12.44));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}](/documents_6/810543cd96960183e939a9377fa60851/img11.jpg)

![namespace ConsoleApplication1
namespace ConsoleApplication1
{
class UserInfo
{
public void ui()
{
Console.WriteLine("Пустой метод\n");
}
public void ui(string Name)
{
Console.WriteLine("Имя пользователя: {0}",Name);
}
public void ui(string Name, string Family)
{
Console.WriteLine("Имя пользователя: {0}\nФамилия пользователя: {1}",Name,Family);
}
public void ui(string Name, string Family, byte Age)
{
Console.WriteLine("Имя пользователя: {0}\nФамилия пользователя: {1}\nВозраст: {2}", Name, Family, Age);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UserInfo user1 = new UserInfo();
user1.ui();
user1.ui("Ерохин", "Александр", 26);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}](/documents_6/810543cd96960183e939a9377fa60851/img13.jpg)
![C# Properties
namespace ConsoleApplication4
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
calculator calc = new calculator();
Console.WriteLine(calc.plus(10,15));
Console.WriteLine(calc.minus(10, 15));
Console.WriteLine(calc.division(10, 15));
Console.WriteLine(calc.multip(10, 15));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
class calculator
{
public int plus(int a,int b) { return a + b; }
public int minus(int a, int b) { return a - b; }
public int division(int a, int b) { return a / b; }
public int multip(int a, int b) { return a * b; }
}
}](/documents_6/810543cd96960183e939a9377fa60851/img14.jpg)