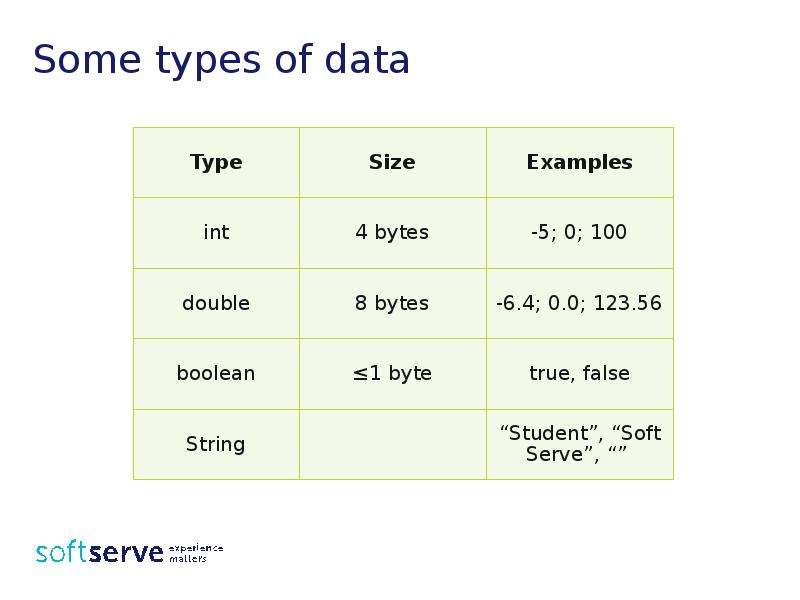
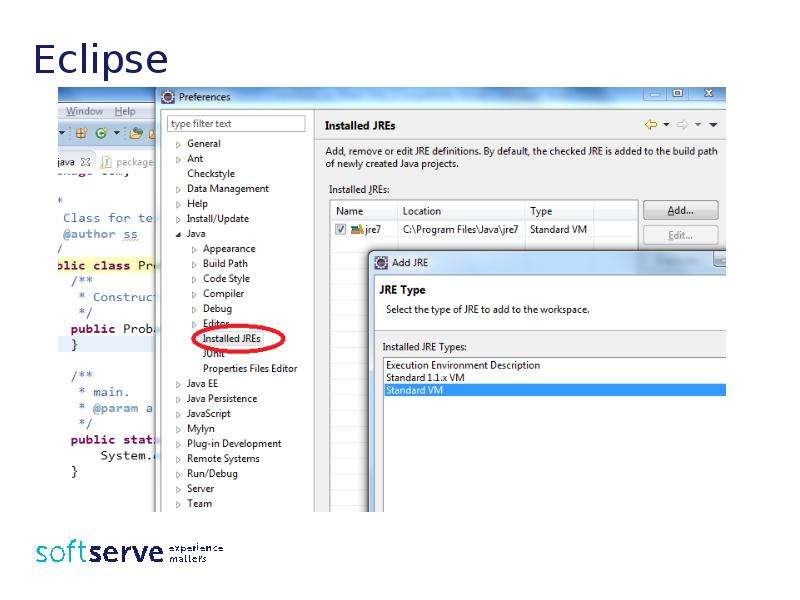
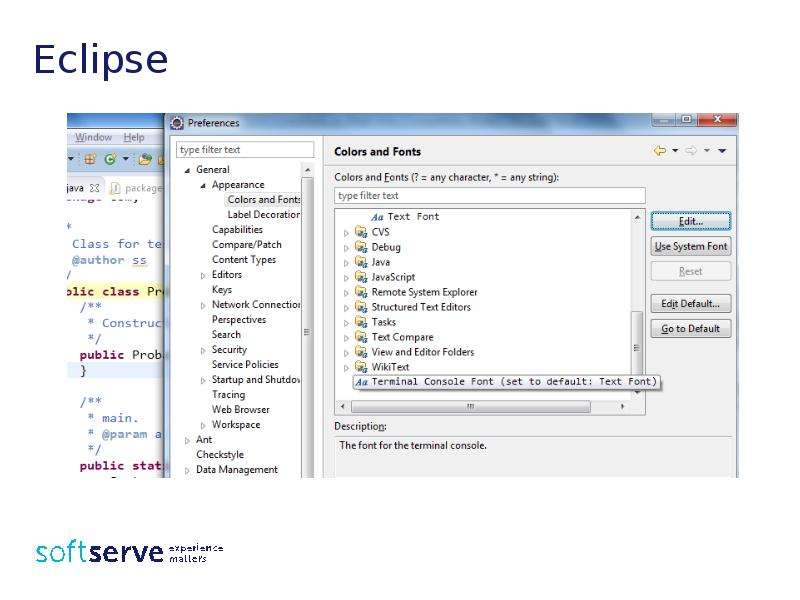
Готовые презентации на тему:
- Образование
- Искусство и Фото
- Наши презентации
- Авто/мото
- Технологии
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Карьера
- Данные и аналитика
- Дизайн
- Устройства и комплектующие
- Экономика и Финансы
- Машиностроение
- Развлечения и Юмор
- Путешествия
- Eда
- Политика
- Юриспруденция
- Здоровье и Медицина
- Интернет
- Инвестиции
- Закон
- Стиль жизни
- Маркетинг
- Мобильные технологии
- Новости
- Недвижимость
- Рекрутинг
- Розничная торговля
- Таможня, ВЭД, Логистика
- Наука
- Услуги
- Программное обеспечение
- Спорт
- Музыка
- Шаблоны презентации
- Детские презентации
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- История
- Литература
- Информатика
- Математика
- Обществознание
- Русский язык
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- МХК
- ОБЖ
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Технология
- Начальная школа
- Раскраски для детей
- Товароведение
- Менеджмент
- Страхование





![Java JDK. Entry Point
public class Example {
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
System.out.println("My first program");
}
}
To display information on the screen it’s used
System.out.println("Text1");
System.out.println("Text 1 " + "Text 2");](/documents_6/f3cfc7ac8113c3879d8900a58fd0d27d/img10.jpg)
![Program Entry Point
public class ShowArgs {
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
for (int i=0; i<args.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Arg " + i + " is " + args[i]);
}
}
}
or
public class ShowArgs2 {
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
for (String arg: args) {
System.out.println("Command line arg: " + arg);
}
}
}](/documents_6/f3cfc7ac8113c3879d8900a58fd0d27d/img13.jpg)






![Packages
Package names and type names usually differ.
package Vector;
public class Mosquito {
int capacity;
}
//- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
package strange.example;
import java.util.Vector;
import Vector.Mosquito;
class Test {
public static void main(String[ ] args) {
System.out.println(new Vector().getClass());
System.out.println(new Mosquito().getClass());
}
}](/documents_6/f3cfc7ac8113c3879d8900a58fd0d27d/img23.jpg)

![My first program
package com.edu;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("Hello. What is your name?");
String name = br.readLine();
System.out.println("How old are you?");
int age = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("Hello " + name);
System.out.println("You are " + age);
}
}](/documents_6/f3cfc7ac8113c3879d8900a58fd0d27d/img25.jpg)