Описание слайда:
Список литературы.
↵ Anonymous. Worldwide variation in prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and atopic eczema: ISAAC. The International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) Steering Committee. Lancet1998;351 (9111) :1225–32.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Wadonda-Kabondo N, Sterne JAC, Golding J, et al. A prospective study of the prevalence and incidence of atopic dermatitis in children aged 0–42 months. Br J Dermatol2003;149 (5) :1023–8.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Eichenfield LF, Hanifin JM, Beck LA, et al. Atopic dermatitis and asthma: parallels in the evolution of treatment. Pediatrics2003;111 (3) :608–16.Abstract/FREE Full TextGoogle Scholar
↵ Kemp AS. Cost of illness of atopic dermatitis in children: a societal perspective. Pharmacoeconomics2003;21 (2) :105–13.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Emerson R, Williams H, Allen B. What is the cost of atopic dermatitis in preschool children? Br J Dermatol2001;143:514–22.Google Scholar
↵ Isolauri E, Arvola T, Sutas Y, et al. Probiotics in the management of atopic eczema. Clin Exp Allergy2000;30:1604–10.PubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Majamaa H, Isolauri E. Probiotics: a novel approach in the management of food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol1997;99:179–85.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Rosenfeldt V, Benfeldt E, Nielsen S, et al. Effect of probiotic Lactobacillus strains in children with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol2003;111 (2) :389–95.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Heller F, Duchmann R. Intestinal flora and mucosal immune responses. Int J Med Microbiol2003;293 (1) :77–86.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Neaville WA, Tisler C, Bhattacharya A, et al. Developmental cytokine response profiles and the clinical and immunologic expression of atopy during the first year of life. J Allergy Clin Immunol2003;112 (4) :740–6.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Lammers KM, Brigidi P, Vitali B, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of probiotic bacteria DNA: IL-1 and IL-10 response in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol2003;38 (2) :165–72.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Sudo N, Sawamura S, Tanaka K, et al. The requirement of intestinal bacterial flora for the development of an IgE production system fully susceptible to oral tolerance induction. J Immunol1997;159:1739–45.AbstractGoogle Scholar
↵ Ball T, Castro-Rodriguez J, Griffith K, et al. Siblings, day-care attendance and the risk of asthma and wheezing during childhood. N Engl J Med2000;343:538–43.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
Kilpi T, Kero J, Jokinen J, et al. Common respiratory infections early in life may reduce the risk of atopic dermatitis. Clin Infect Dis2002;34:620–6.Abstract/FREE Full TextGoogle Scholar
↵ Sherriff A, Golding J. Hygiene levels in a contemporary population cohort are associated with wheezing and atopic eczema in preschool infants. Arch Dis Child2002;87 (1) :26–9.Abstract/FREE Full TextGoogle Scholar
↵ Matricardi PM, Bjorksten B, Bonini S, et al. Microbial products in allergy prevention and therapy. Allergy2003;58 (6) :461–71.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
Bottcher M, Nordin E, Sandin A, et al. Microflora-associated characteristics in faeces from allergic and nonallergic infants. Clin Exp Allergy2000;30 (11) :1590–6.PubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ von Mutius E, Braun-Fahrlander C, Schierl R, et al. Exposure to endotoxin or other bacterial components might protect against the development of atopy. Clin Exp Allergy2000;30 (9) :1230–4.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
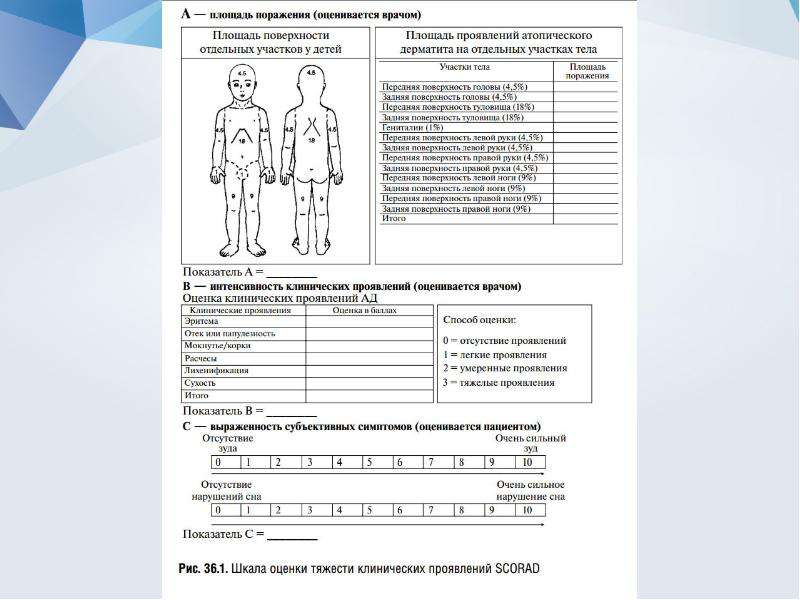
↵ Anonymous. Severity Scoring of Atopic Dermatitis: the SCORAD index. Consensus report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology1993;186 (1) :23–31.PubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Hanafin J, Raijka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh)1980;92:44–7.Google Scholar
↵ Kunz B, Oranje A, Labreze L, et al. Clinical validation and guidelines for the SCORAD index: consensus report of the European Task Force on Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatology1997;195 (1) :10–19.PubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Marley J, Baker CS, English J, eds. Getting to know your drugs. In: Therapeutic Guidelines: Dermatology. Version 2, 2004. North Melbourne, Australia: Therapeutic Guidelines, 2004:35.Google Scholar
↵ Lawson V, Lewis-Jones MS, Finlay AY, et al. The family impact of childhood atopic dermatitis: the Dermatitis Family Impact Questionnaire. Br J Dermatol1998;138 (1) :107–13.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Illi S, von Mutius E, Lau S, et al. The natural course of atopic dermatitis from birth to age 7 years and the association with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol2004;113 (5) :925–31.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar
↵ Murch SH. Toll of allergy reduced by probiotics. Lancet2001;357 (9262) :1057–59.CrossRefPubMedWeb of ScienceGoogle Scholar